Mirror Bore Coating
Reducing drag inside the engine and improving fuel consumption and power
Engine energy efficiency is a major influence on fuel consumption and engine performance. There are several factors that lower energy efficiency; one is mechanical loss. Energy efficiency drops due to the friction that arises from mechanical parts rubbing against each other. Mirror bore coating is a technology that raises energy efficiency by reducing the friction inside the engine.

Technology Functionality
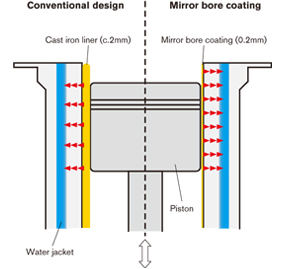
Many engines today use lightweight aluminum materials for the cylinder block. In the cylinder block there is a cylindrical space inside which the piston moves up and down. However, since aluminum cannot endure the friction and heat that arises, designs also use a cast iron cylinder liner.
Rather than inserting a cylinder liner, though, mirror bore coating technology sprays molten iron onto the surface of the cylinder bore and forms an iron coating layer on the walls inside. By giving this a mirror-like finish, the drag that arises when the piston is operating can be reduced. The main purpose of this technology is to reduce drag, though there are other merits as well. Firstly, by removing the cylinder liner the design realizes a lighter engine.
Moreover, compared to the roughly 2mm-thick cylinder liner, the 0.2mm mirror bore coating is extremely thin, making for better heat conduction. This results in better cooling performance and less engine knocking, and the efficiency of the engine as a whole is improved. The leeway gained can go towards increasing fuel economy and engine power.
Mirror bore coating is able to improve the fundamental performance of the engine without the need for a special device.
Technology Configuration
Technology for coating the inside of the cylinder bore has existed for a long time. However, the technology was very labor-intensive and so was only utilized for racing cars or high-end sports cars. Nissan was able to apply the technology for its GT-R vehicle. Through unique technology that pretreats the aluminum surface by spraying molten iron, Nissan could achieve a large reduction in the cost of the technology. This meant that the technology could be employed in mass-produced engines without an increase in cost.

(Left) A cast iron liner and conventional four-cylinder engine. (Right) A new type of four-cylinder engine with mirror bore coating.

