Lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles
For many years, Nissan has been working on the development of lithium-ion batteries, which are the key to electric vehicles, and launched the first Nissan LEAF in 2010 as a pioneer of mass-produced EVs. Nissan has continued to evolve its performance as well as high reliability.
Lithium-ion batteries have higher energy densities than lead-acid batteries and nickel-metal hydride batteries, making it possible to reduce their size while retaining the same storage capacity.
Nissan's lithium-ion battery technology utilizes electrode materials that allow a higher density of lithium ions to be stored in a pack structure, which improves layout efficiency. This enables an increase in battery storage capacity.
System mechanism
Positive electrode material
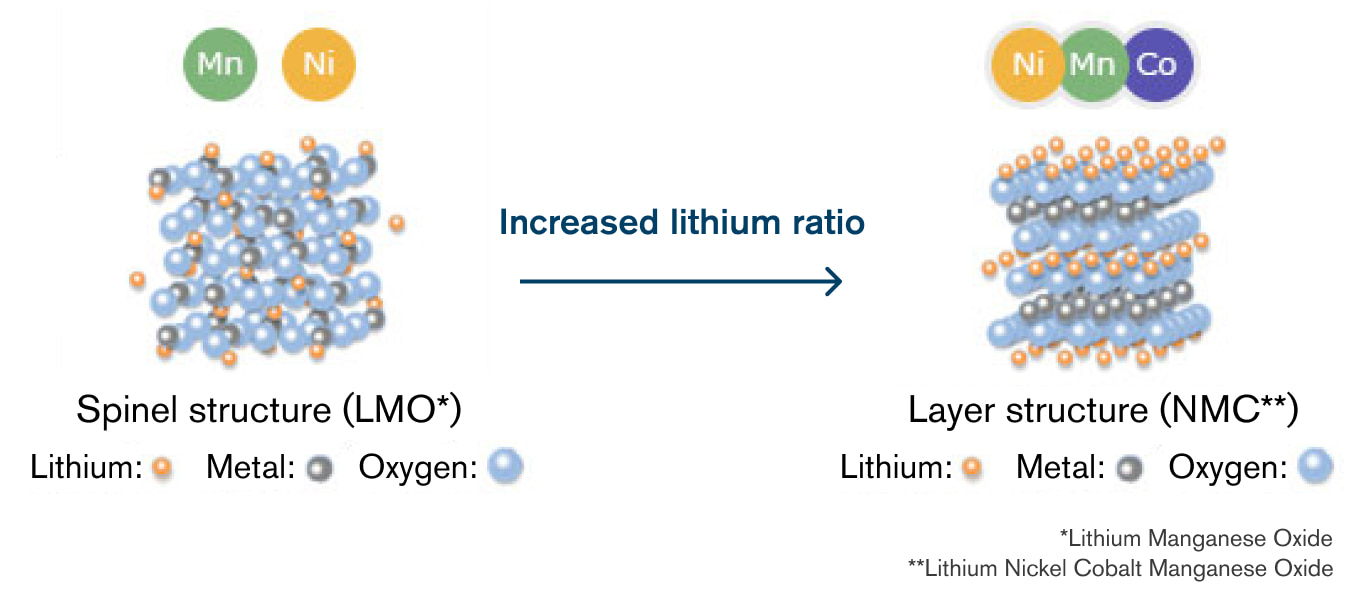
The first-generation LEAF used manganese-based cathode material, but later this was changed to ternary cathode material to achieve a high energy density.
Ni-Co-Mn material has a layered structure so it can store lithium ions at a high density, contributing to an increase in battery capacity.
Pack structure
The pack structure includes a universal stack structure that is customizable to support a variety of platforms and a flat battery structure to support CMF-EV platform.
1. Universal stack structure
The battery cell is laminated and has a simple structure design and high cooling performance. Originally, an 8-cell module structure composed of eight individual cells was utilized. Due to the fixed height of the module, the mounting layout was limited and the vehicle platform space could not be optimally used. Therefore, engineers developed a universal stack structure that added enhanced customization including the number of cell numbers and packaging layout. By using laser welding to join cells, each module's overall dimensions (length and height) were reduced, allowing for the development of optimal battery module shapes to best fit EV platforms and meet customer needs.

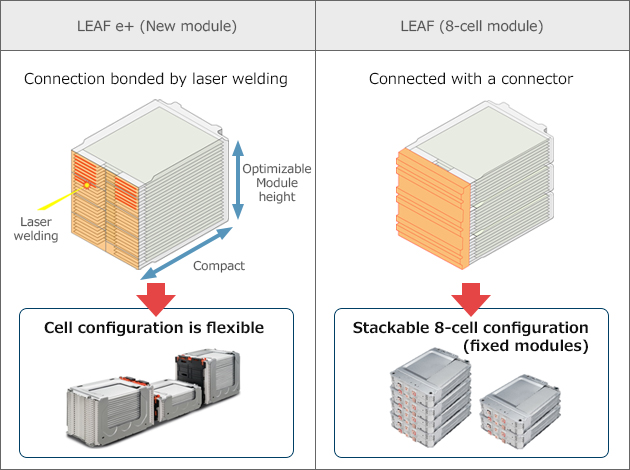
A major benefit in using a universal stack structure is the ability to fit the battery pack in optimal areas of the vehicle such under the floor or under rear seating. This helps to maximize the usable interior space, making even the cabin area of smaller vehicles feel more spacious.
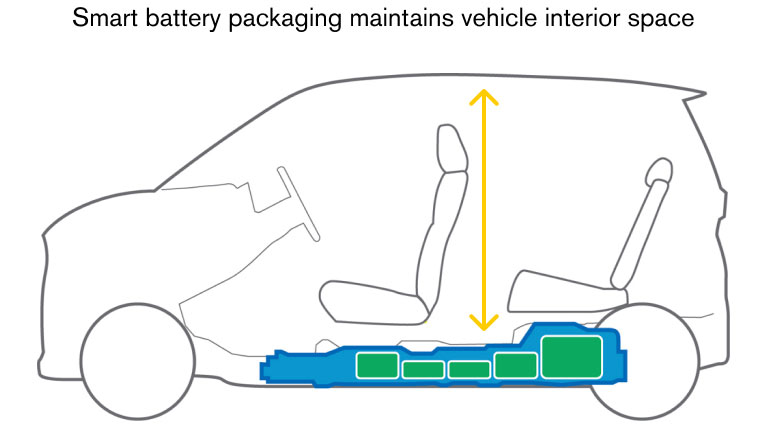
2. Large-capacity flat battery structure for CMF-EV platform
A flat battery structure with large modules is utilized to ensure sufficient battery capacity while allowing a flat floor and ample legroom.
Designing a flatter floor and increasing energy capacity
A typical car chassis features cross members to increase strength and rigidity at the expense of a floor that is uneven.
By using a large-capacity flat battery structure that is designed to have increased pack rigidity and optimizing floor fastening points, a flat floor can be achieved that also houses large battery modules.
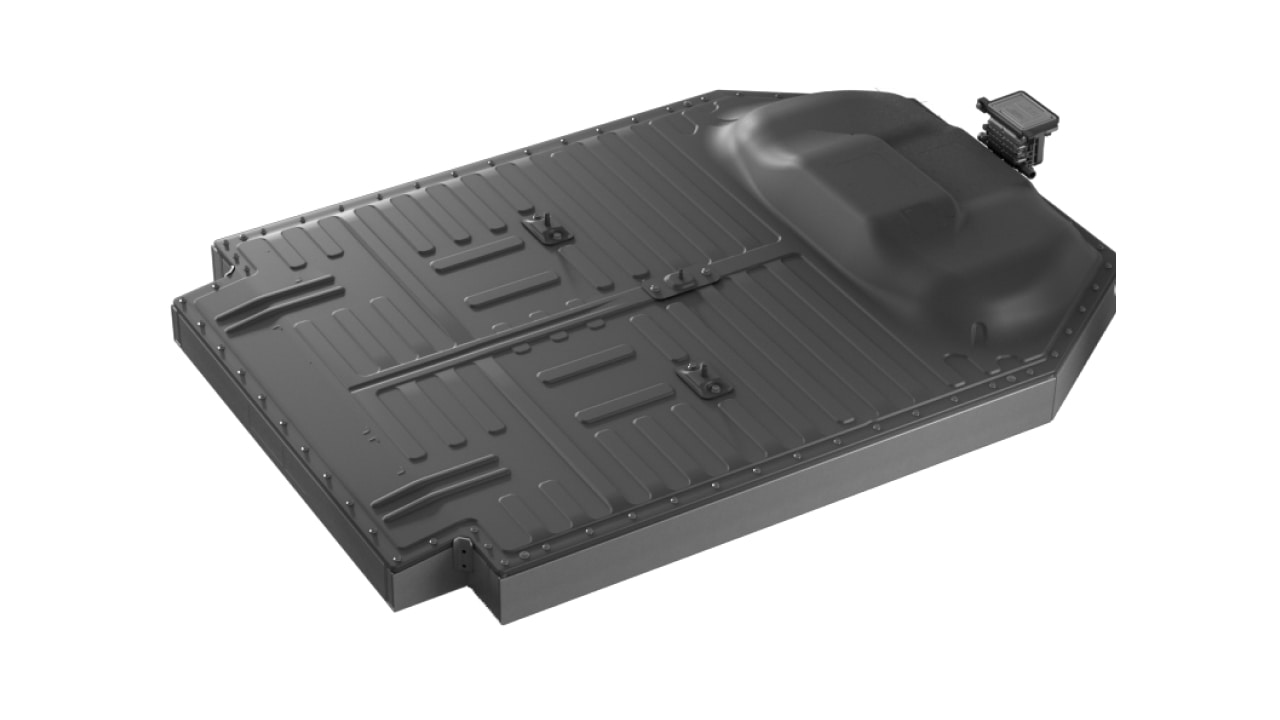

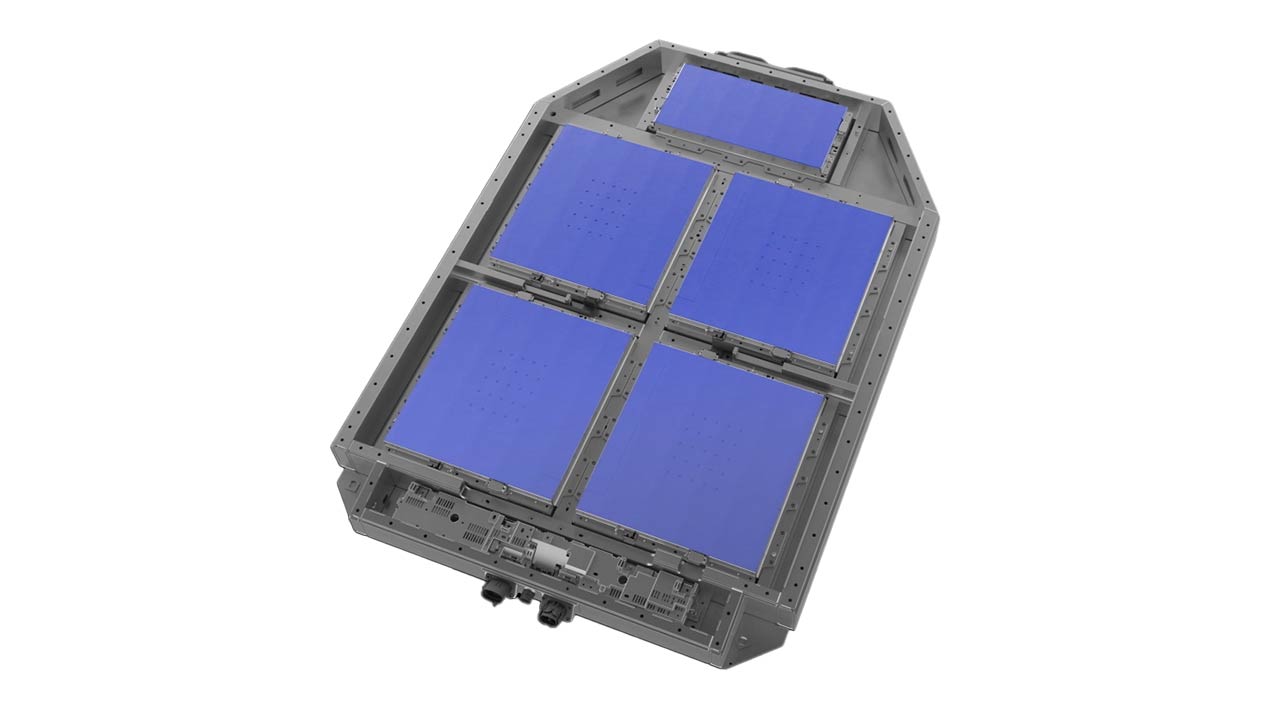
3rd gen LEAF battery
Low-profile, temperature controlled structure
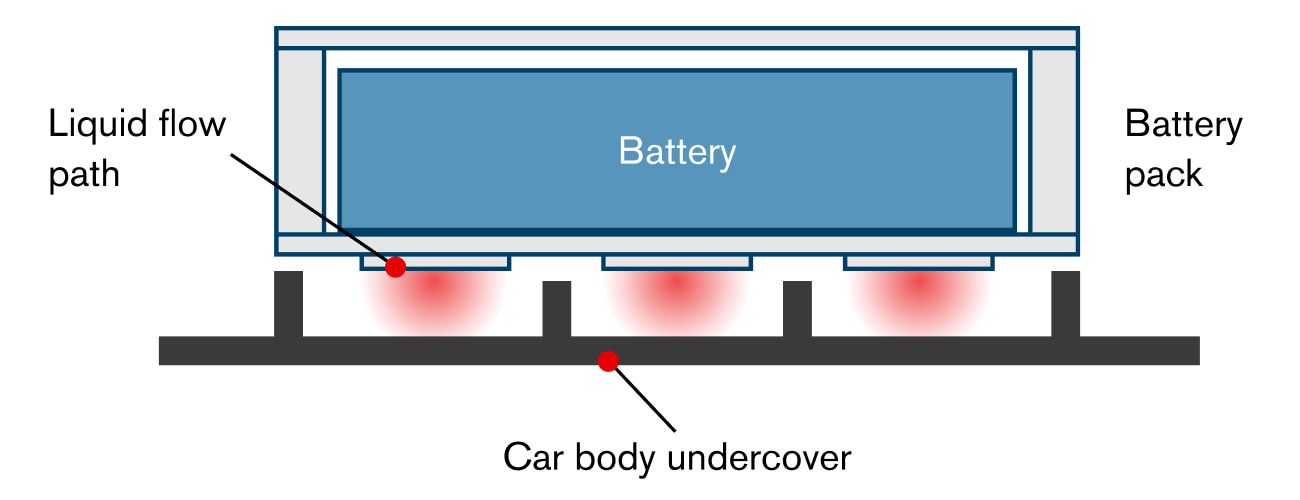
Integrating a liquid flow path throughout the bottom of the pack enables the battery to be cooled and heated evenly while maintaining its thin shape. The temperature can also be adjusted to best suit driving conditions.
Additionally, in the 3rd generation LEAF, the shape of the undercover below the battery blocks the flow of air, improving thermal insulation and maintaining optimal battery pack temperature. This can also improve energy efficiency.