Ultra High Tensile Strength Steel with High Formability
This material achieves both high strength and elongation capacity while also reducing vehicle body structure weight
Vehicle
weight
and
size
have
been
increasing
in
recent
years
with
the
pursuit
of
safety
and
comfort.
Weight
reduction
is
an
unavoidable
path
for
auto
manufacturers,
in
order
to
improve
fuel
consumption
and
reduce
CO2
emissions.
Nissan
has
dedicated
itself
to
developing
new
materials
to
reduce
a
vehicle’s
overall
weight.
In
order
to
simultaneously
clear
the
two
issues
of
“reducing
vehicle
weight
to
reduce
environmental
impact”
and
“improving
collision
safety”,
Nissan
has
focused
on
using
high
tensile
strength
steel
in
their
vehicle
body
structures.
The
results
are
body
structures
that
are
not
only
strong
but
also
highly
formable.
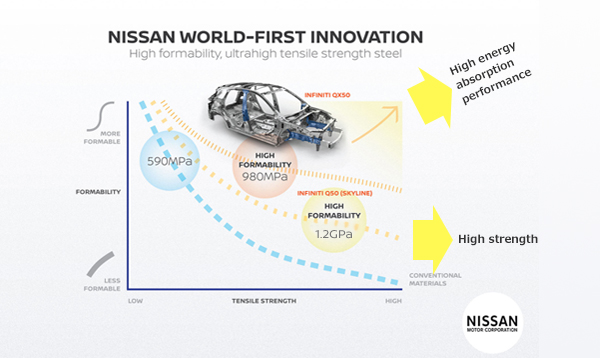
In
2013,
Nissan
succeeded
in
developing
a
1.2
Gpa
ultra
high
tensile
strength,
high-formability
steel
that
was
stronger
than
conventional
high
tensile
steels.
This
new
material
was
first
used
in
the
Infiniti
Q50
midsize
sedan.
In
2018,
Nissan
developed
and
introduced
a
980
MPa
ultra
high
tensile
strength,
high-formability
steel
that
featured
further
improvements
to
collision
energy
absorption
performance.
This
material
was
used
in
the
Infiniti
QX50
premium
midsize
SUV.
Research
and
development
efforts
such
as
Ultra
High
Tensile
Strength
Steel
have
resulted
in
further
reducing
vehicle
weight
and
improving
collision
safety.
System operation
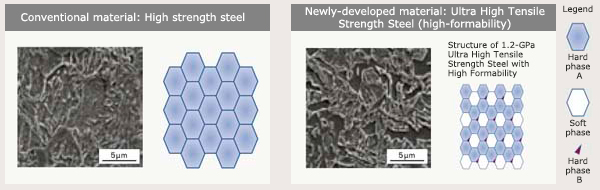
- As a general rule, when the strength of high tensile steel is increased, its elongation capacity decreases. A decrease in elongation capacity can cause cracking during cold-press forming. Because prior high tensile strength steels were unable to withstand cold-pressing into complex shapes, they were used only for a limited number of parts.
- The advantage of 1.2-GPa Ultra High Tensile Strength Steel with High Formability is to have both high strength and elongation capacity. By precisely controlling the material’s structure on the sub-micron level through a new heat treatment process, it can be utilized for many more body structure parts than previously possible.
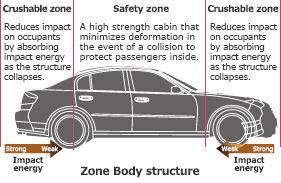
- A spot welding method suitable for 1.2-GPa Ultra High Tensile Strength Steel with Formability has also been developed. The new welding method makes it possible to use this steel for “Safety Zone” structure parts, such as the center pillar reinforcement, front roof rails, and side roof rails, meant to protect vehicle occupants in the event of a collision.
- For the newly developed 980-MPa Ultra High Tensile Strength Steel with High Formability, a more finely tuned heat treatment process that gives the material high energy absorption performance was achieved. As a world-first, Nissan began using this material on the front side members, rear side members, and other “crushable zone” frame parts that require high collision energy absorption. This material has the same level of formability as conventional 590-MPa steel, and can be used for parts with more complex shapes.
Nissan has established a target of using Ultra High Tensile Strength Steel with High Formability in 25% or more of the gross weight of body parts. Nissan is actively moving forward with the development of technologies for applications of high strength steel and expands its use in the Nissan model line-up.